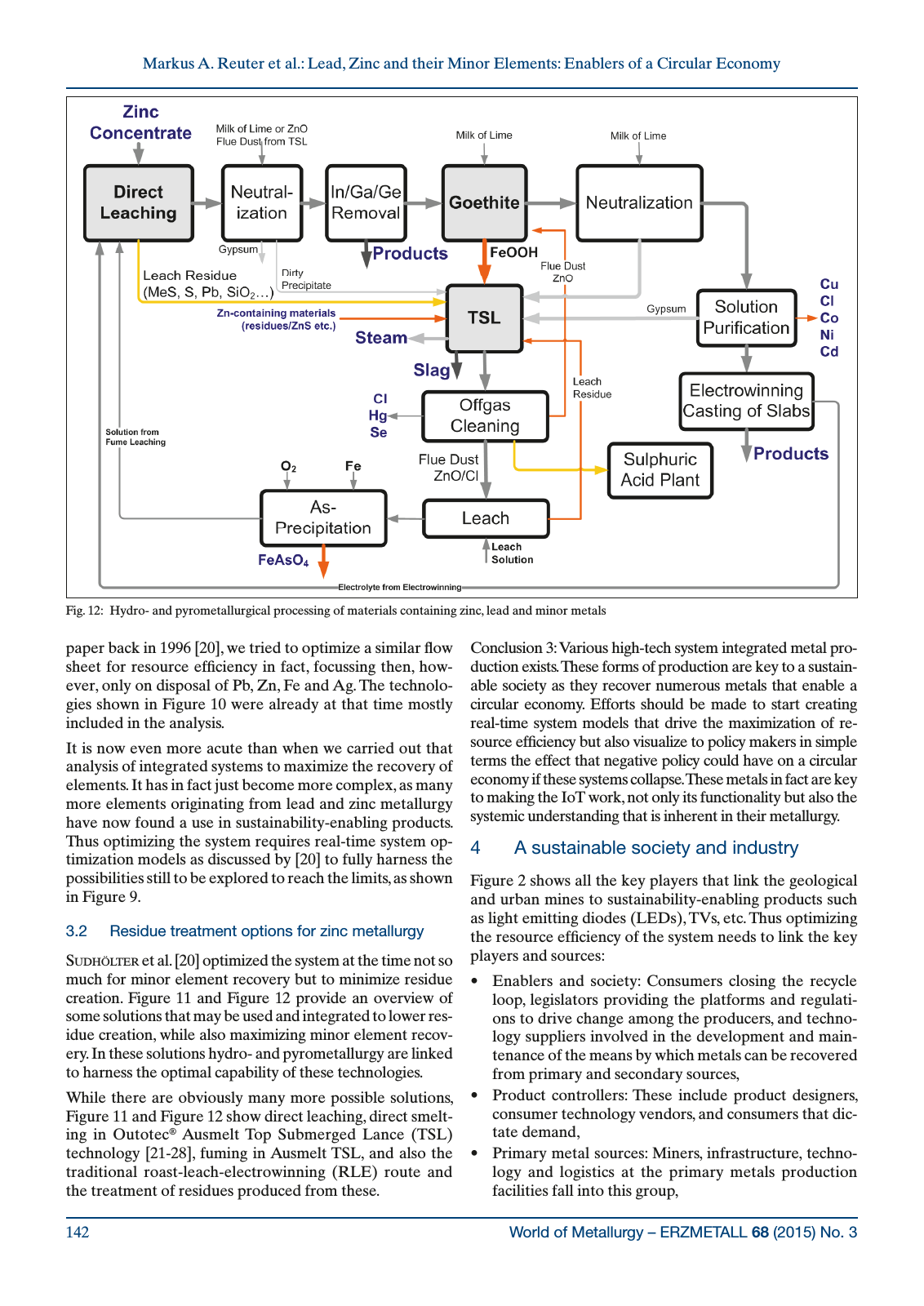
World of Metallurgy ERZMETALL 68 2015 No 3142 Markus A Reuter et al Lead Zinc and their Minor Elements Enablers of a Circular Economy paper back in 1996 20 we tried to optimize a similar flow sheet for resource efficiency in fact focussing then how ever only on disposal of Pb Zn Fe and Ag The technolo gies shown in Figure 10 were already at that time mostly included in the analysis It is now even more acute than when we carried out that analysis of integrated systems to maximize the recovery of elements It has in fact just become more complex as many more elements originating from lead and zinc metallurgy have now found a use in sustainability enabling products Thus optimizing the system requires real time system op timization models as discussed by 20 to fully harness the possibilities still to be explored to reach the limits as shown in Figure 9 3 2 Residue treatment options for zinc metallurgy Sudhölter et al 20 optimized the system at the time not so much for minor element recovery but to minimize residue creation Figure 11 and Figure 12 provide an overview of some solutions that may be used and integrated to lower res idue creation while also maximizing minor element recov ery In these solutions hydro and pyrometallurgy are linked to harness the optimal capability of these technologies While there are obviously many more possible solutions Figure 11 and Figure 12 show direct leaching direct smelt ing in Outotec Ausmelt Top Submerged Lance TSL technology 21 28 fuming in Ausmelt TSL and also the traditional roast leach electrowinning RLE route and the treatment of residues produced from these Conclusion 3 Various high tech system integrated metal pro duction exists These forms of production are key to a sustain able society as they recover numerous metals that enable a circular economy Efforts should be made to start creating real time system models that drive the maximization of re source efficiency but also visualize to policy makers in simple terms the effect that negative policy could have on a circular economy if these systems collapse These metals in fact are key to making the IoT work not only its functionality but also the systemic understanding that is inherent in their metallurgy 4 A sustainable society and industry Figure 2 shows all the key players that link the geological and urban mines to sustainability enabling products such as light emitting diodes LEDs TVs etc Thus optimizing the resource efficiency of the system needs to link the key players and sources Enablers and society Consumers closing the recycle loop legislators providing the platforms and regulati ons to drive change among the producers and techno logy suppliers involved in the development and main tenance of the means by which metals can be recovered from primary and secondary sources Product controllers These include product designers consumer technology vendors and consumers that dic tate demand Primary metal sources Miners infrastructure techno logy and logistics at the primary metals production facilities fall into this group Fig 12 Hydro and pyrometallurgical processing of materials containing zinc lead and minor metals Figure 12 Reuter
Hinweis: Dies ist eine maschinenlesbare No-Flash Ansicht.
Klicken Sie hier um zur Online-Version zu gelangen.
Klicken Sie hier um zur Online-Version zu gelangen.