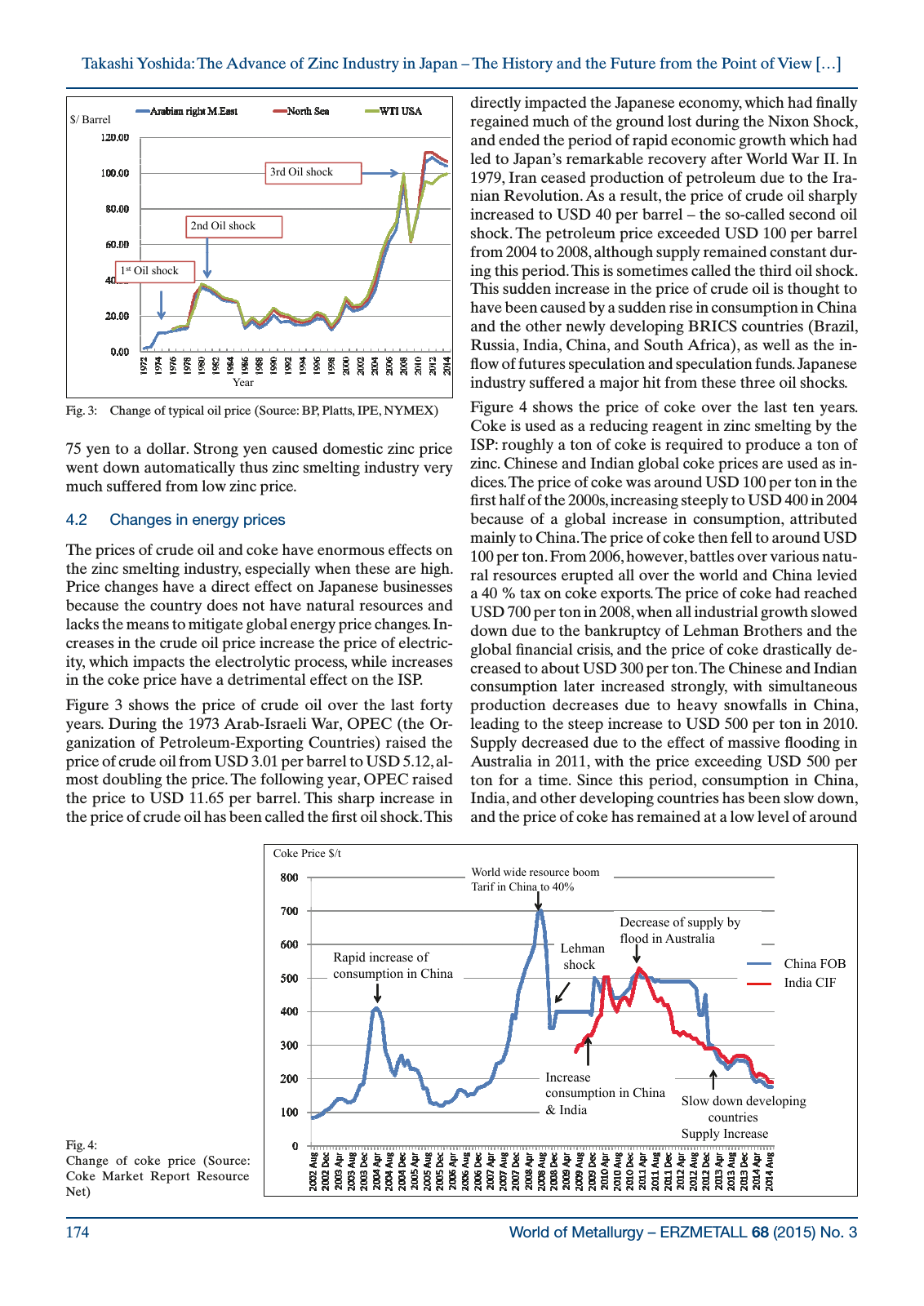
World of Metallurgy ERZMETALL 68 2015 No 3174 Takashi Yoshida The Advance of Zinc Industry in Japan The History and the Future from the Point of View 75 yen to a dollar Strong yen caused domestic zinc price went down automatically thus zinc smelting industry very much suffered from low zinc price 4 2 Changes in energy prices The prices of crude oil and coke have enormous effects on the zinc smelting industry especially when these are high Price changes have a direct effect on Japanese businesses because the country does not have natural resources and lacks the means to mitigate global energy price changes In creases in the crude oil price increase the price of electric ity which impacts the electrolytic process while increases in the coke price have a detrimental effect on the ISP Figure 3 shows the price of crude oil over the last forty years During the 1973 Arab Israeli War OPEC the Or ganization of Petroleum Exporting Countries raised the price of crude oil from USD 3 01 per barrel to USD 5 12 al most doubling the price The following year OPEC raised the price to USD 11 65 per barrel This sharp increase in the price of crude oil has been called the first oil shock This directly impacted the Japanese economy which had finally regained much of the ground lost during the Nixon Shock and ended the period of rapid economic growth which had led to Japan s remarkable recovery after World War II In 1979 Iran ceased production of petroleum due to the Ira nian Revolution As a result the price of crude oil sharply increased to USD 40 per barrel the so called second oil shock The petroleum price exceeded USD 100 per barrel from 2004 to 2008 although supply remained constant dur ing this period This is sometimes called the third oil shock This sudden increase in the price of crude oil is thought to have been caused by a sudden rise in consumption in China and the other newly developing BRICS countries Brazil Russia India China and South Africa as well as the in flow of futures speculation and speculation funds Japanese industry suffered a major hit from these three oil shocks Figure 4 shows the price of coke over the last ten years Coke is used as a reducing reagent in zinc smelting by the ISP roughly a ton of coke is required to produce a ton of zinc Chinese and Indian global coke prices are used as in dices The price of coke was around USD 100 per ton in the first half of the 2000s increasing steeply to USD 400 in 2004 because of a global increase in consumption attributed mainly to China The price of coke then fell to around USD 100 per ton From 2006 however battles over various natu ral resources erupted all over the world and China levied a 40 tax on coke exports The price of coke had reached USD 700 per ton in 2008 when all industrial growth slowed down due to the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers and the global financial crisis and the price of coke drastically de creased to about USD 300 per ton The Chinese and Indian consumption later increased strongly with simultaneous production decreases due to heavy snowfalls in China leading to the steep increase to USD 500 per ton in 2010 Supply decreased due to the effect of massive flooding in Australia in 2011 with the price exceeding USD 500 per ton for a time Since this period consumption in China India and other developing countries has been slow down and the price of coke has remained at a low level of around Fig 3 Change of typical oil price Source BP Platts IPE NYMEX Barrel 3rd Oil shock 2nd Oil shock 1 st Oil shock YearY Fig 4 Change of coke price Source Coke Market Report Resource Net Coke Price t World wide resource boom Tarif in China to 40 Decrease of supply by Rapid increase of consumption in China Lehman shock flood in Australia China FOB I di CIFn a Increase consumption in China India Slow down developing countries Supply Increase
Hinweis: Dies ist eine maschinenlesbare No-Flash Ansicht.
Klicken Sie hier um zur Online-Version zu gelangen.
Klicken Sie hier um zur Online-Version zu gelangen.